Table of contents
- What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
- Benefits of Calculating Return On Investment (ROI)
- How to Calculate ROI (ROMI) and ROAS with Examples
- Factors to Remember for Assessing ROI Calculation Results
- Overcoming Limitations of Calculating Return On Investment (ROI)
- Method of Calculating Annual Return On Investment
- Alternative to the ROI Formula: The Rate of Return On Investment
- How to automate ROI and ROAS calculation with OWOX BI
- What is considered a good ROI?
- Expanding the Scope of ROI: Beyond Traditional Metrics
- Conclusion
How to Calculate Return on Investment for Marketing Campaigns in 2024
Liubov Zhovtonizhko, Creative Writer @ OWOX
Denis Lisogorja, Web analyst @ OWOX
We’ve already discovered about the definition of one of the most important metrics for business: the lifetime value of a customer, or LTV.

In this article, originally published in January 2021 and completely updated in January 2024, we’ll tell you about another important indicator and its meaning: ROI.
With it, you can identify effective channels to attract customers and, as a result, more wisely manage your budget for advertising campaigns.
What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on investment (ROI) is a very important metric that measures the efficiency of various investments. It is a measure that contrasts the gains or losses from an investment against its original cost.
In marketing, this ratio is pivotal for measuring the success of efforts and investments, be it in evaluating the impact of a marketing campaign, determining the return on a product launch, or analyzing the profitability of a new promotional strategy. It helps in making informed decisions about where and how to allocate marketing resources for maximum effectiveness.
The definition of ROI is a ratio of income from an investment to the expenses to finance that investment. The higher the ratio is, the more benefit you earn. It is a measure that contrasts the gains or losses from an investment against its original cost.
ROI is often confused with two other similar metrics: ROMI and ROAS.
ROMI is an indicator of marketing ROI that is used to measure the overall effectiveness of all marketing activities and helps marketers better allocate marketing budgets. It is calculated as the ratio of income from marketing efforts to marketing costs (salary, etc.).
ROAS, or return on ad spend, is commonly used to measure the performance of a particular campaign, ad group, particular ad, or even a single keyword. With ROAS, you can evaluate any aspect of your internet marketing activities. Want to know if a particular ad set is worth your time and money? Check your ROAS. Want to know if the targeting changes you've made are working? Check your ROAS.
Often ROAS and ROMI are expressed as a percentage, but sometimes in the form of a coefficient. We have discussed both of these in detail below with formulas and examples.
Automate Marketing Reporting
With OWOX BI you can automate your entire marketing reporting: ad campaigns, Cohorts and RMF, ROPO, LTV, CAC or attribution
Benefits of Calculating Return On Investment (ROI)
The primary advantage of calculating Return on Investment (ROI) lies in its extreme ease of understanding:
- This metric is simple to compute and inherently easy to grasp, making it an accessible and clear measure of profitability. Its simplicity has led to ROI being universally recognized and adopted as a standard for assessing financial success.
- The consistency of its meaning across various contexts reduces the likelihood of misinterpretation or confusion, ensuring that it is uniformly understood in every application.
- Different businesses have varying benchmarks for ROI: some can profit from a low ROI, while others require a high ROI to ensure they don't lose money on digital advertising.
- Monitoring the trends in reports allows for strategic budget allocation for more effective advertising channels.
- If a company's spending on Google Ads does not yield a positive return, it's advisable to reallocate funds to more profitable channels. For instance, if the Google organic channel proves more effective, redirecting investment from Google Ads to this channel could increase revenue.
How to Calculate ROI (ROMI) and ROAS with Examples
ROI can be calculated using one of two approaches.
1. The first approach is:
This formula calculates ROI by dividing the net return on the investment by the initial cost of the investment, then multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage.
2. The second approach is:
Where:
- FVI stands for the final value of the investment.
- IVI represents the initial value of the investment.
In this method, ROI is determined by subtracting the initial value of the investment from the final value, dividing this by the cost of the investment, and then multiplying by 100 to convert it into a percentage.
Examples of How to Calculate Return On Investment and ROMI
Let’s look at an example for a better understanding of how to calculate return on investment.
Imagine you sell a product through your site. You have a budget that you’re willing to spend on Google Ads. Suppose it’s $1,000 per month. You launch a campaign, everything is going fine, and by the end of the month, your income from advertising campaigns is $6,000.
The formula for calculating ROAS is:
Let’s calculate ROAS based on our example: $6000 / $1000 х 100% = 600%
So for every dollar you spend, you earn $6 in profit. Not bad for advertising on one channel.
To calculate return on investment, you need to include salaries and all associated marketing costs. For example, say you paid $200 for a PPC specialist to set up this ad plus $50 to the copywriter who wrote the ad.
The general formula for calculating ROI:
ROI calculation: ($6000 — ($1000 + $200 + $50) / ($1000 + $200 + $50)) x 100% = 380%
What does this mean for you? Well, it means that for every dollar you spent, you earned $3.8 in profit.
Although ROI (ROMI) and ROAS are similar, it is important not to confuse these indicators, as this can lead to serious mistakes. ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) specifically measures the revenue generated from each dollar spent on advertising, while ROI (Return on Investment) is a broader metric that assesses the overall profitability of an investment, encompassing all costs and revenues.
For example, ROI of 100% means that you earned twice as much as you spent. But ROAS of 100% means that you have broken even.
It seems that everything is simple and easy to calculate. But for a more correct ROI calculation, a marketer needs to take into account many nuances.
Measure CPO and ROAS in GA4
Automatically link your Ad Platforms cost data to Google Analytics 4 conversion data, so you can analyze your marketing KPIs and make fully informed decisions
4.9
Factors to Remember for Assessing ROI Calculation Results
When assessing ROI calculations, several key points should be noted.
- Firstly, ROI is commonly expressed as a percentage for its ease of understanding compared to a ratio.
- Secondly, the numerator in the ROI formula accounts for the net return, which acknowledges that investment returns can be either positive or negative.
- A positive ROI indicates that the net returns are profitable, meaning the total returns surpass the total costs. Conversely, a negative ROI signifies a loss, where the total costs exceed the total returns.
- For the most accurate ROI calculation, it's crucial to include all total returns and costs. To make a fair comparison between different investment options, the annualized ROI should be taken into account.
While the ROI formula may appear straightforward, it relies heavily on precise cost accounting. This is relatively straightforward for investments like stock shares but can be more complex for other scenarios, such as evaluating the ROI of a potential business project.
Overcoming Limitations of Calculating Return On Investment (ROI)
At first glance, ROI is a simple and understandable indicator that can be calculated without problems, but there are a few nuances to keep in mind.
1. Attribution Challenges in Calculating ROI
In a simple case, a user clicks on an ad and makes a purchase. This revenue belongs to the ROI calculation we’ve mentioned above. But what if the user clicks but doesn’t buy right then? What if someone clicks on your ad, goes to your website but closes it, then three weeks later sees a post for your product on Facebook, clicks on it, goes to your website, memorizes the URL and closes the site, and then a month later goes directly to your website by typing in the URL and makes a purchase? You could argue that this customer should be counted in the calculation for the initial ad because they first found your store via that ad campaign. Or you could argue that the Facebook post should get the credit since that was the last click before the purchase. A third option would be to split the revenue between the initial ad and the Facebook post.
The attribution model you choose determines how much credit your initial ad gets for this customer. What’s important is that you pick a single attribution model and use it consistently when comparing ROAS across channels and campaigns.
To objectively distribute the value of an order, it’s necessary to evaluate not just the last session but each buyer session. This is why we suggest using an ML attribution model.
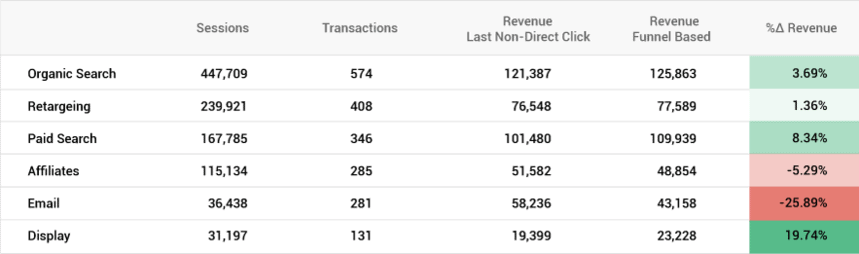
Take a look at the report below that we’ve created for one of our clients. We found that the value (revenue from orders) assigned to advertising channels as a result of funnel-based attribution differs from that obtained by using the Last Non-Direct Click model. That is, if you use Last Non-Direct Click attribution model, ROAS will be different from the real numbers.
2. Take into account all factors affecting revenue
Let’s take a look at a couple of things that might affect revenue.
Your best sales manager has switched to another company. You’ve changed a supplier, affecting the timing of delivery for certain goods. At the same time, you’ve launched an advertising campaign and have many potential buyers — but there are no goods available. As a result, you have decreased ROMI, but this has nothing to do with advertising and marketing.
To find a real-life example of the importance of a funnel-based attribution model, read our case study on how a company optimized ad spend by creating an effective campaign scoring system.
3. Addressing the Time Factor in ROI Calculations to Enhance Accuracy
One of the crucial aspects to consider when overcoming limitations in calculating Return on Investment (ROI) is the incorporation of the time factor. Unlike traditional ROI calculations, which might not distinguish between returns generated over different time spans, a more nuanced approach is required for accurate assessment. For instance, two investments might both show an ROI of 50%, but if one achieves this in three years and the other in five, the time factor significantly influences which is the better option. To address this, investors should compare investment returns over identical time periods, ensuring a more accurate and meaningful evaluation of ROI. This approach helps in recognizing the true efficiency of an investment by considering the duration it takes to yield returns, thereby providing a more comprehensive analysis of an investment's performance.
4. Account for differences in costs (hard to calculate the average check)
A significant limitation in calculating Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI) arises from fluctuating and diverse costs, which can distort the true effectiveness of a marketing strategy. Costs like shipping fees can vary significantly over time or between different customer segments, leading to challenges in accurately determining ROMI. To overcome this, it's essential to continuously update and incorporate all variable costs into the ROMI calculation. This approach ensures that the calculated ROMI reflects the current cost structure and market conditions, providing a more accurate measure of marketing strategy effectiveness.
Imagine this. Last month you paid $100 to ship an order to Europe. But this month, your shipping service has raised their prices and now you need to pay $100 for shipping to US customers and $200 for shipping the same product to European customers. Or perhaps your customers pre-ordered some expensive products due to an ad on Facebook. As a result, your ROMI may decline, although your marketing strategy is correct.
Method of Calculating Annual Return On Investment
The Annual Return on Investment (ROI) formula is crucial for accurately assessing investment performance over time. Unlike the standard ROI, which doesn't account for the investment period, the annualized ROI provides a time-adjusted rate of return. This adjustment is particularly important for comparing returns over different periods, offering a more consistent benchmark. The annualized ROI formula considers this time factor, offering a more nuanced and accurate measure of an investment's efficiency and profitability.
One of the disadvantages of the regular return on investment calculation is that it doesn’t consider time periods. For example, a 20% return for 3 years is the same as a 20% return for 3 days, even though a 20% return in 3 days is better than 3 years. To deal with this issue, use an annualized ROI formula.
For example, if you invest $10 in advertising on January 1, 2023 for $10 and receive $12 revenue from it on June 25, 2023, the regular and annualized formulas will be the following:
Regular formula = ($12 – $10) / $10×100%= 20%
Annualized formula = [ ($12 / $10) ^ (1 / ((Jun 25 – Jan 1)/365)) ] −1 = 0.46 or 46%
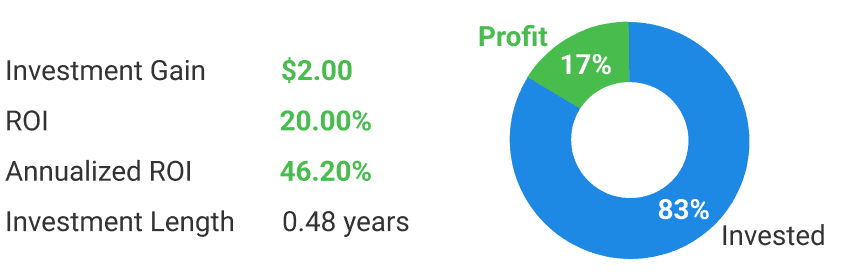
Therefore, even though a regular return on investment ratio is 20%, the same figures in longer perspective give you more profit. The annualized rate of return and annual return differ because the former one also includes the sum of investment earnings over time.
Alternative to the ROI Formula: The Rate of Return On Investment
When we talk about how well our investments are doing, we usually hear about things like Rate of Return (RoR) and Return on Investment (ROI). They're like the financial world's dynamic duo, both zooming in on how profitable our investments are. Think of RoR as the detail-oriented one: it shows the percentage gain or loss from your original investment, often spread out over time to make it easier to compare. ROI, on the other hand, takes a step back for a bigger picture. It considers the total cash you've made compared to what you spent, and it's not tied to any specific time frame. Both of these metrics are super handy for figuring out if your investments are really paying off.
Now, let's chat about alternatives to ROI. Each has its own unique way of sizing things up.
RoR is like the Swiss Army knife of measuring returns. Whether it's real estate, stocks, bonds, or even that pricey piece of art you bought, RoR can handle it. It's great for any asset where you put down cash at one point and then watch the money roll in later.
Especially in the marketing world, RoR is a big deal. It's like having a microscope to zoom in on how much bang you're getting for your buck. Digital ads, old-school billboards, social media shenanigans – you name it, RoR can tell you how well they're working.
Take online ads, for example. By crunching the numbers on how much you spent versus what you gained, RoR helps you figure out which platforms are the real MVPs in terms of making money. And it's not just about immediate sales – RoR can show you the long game too, like how your blog posts or SEO efforts are playing out in the grand scheme of things.
In a nutshell, RoR helps you see the big picture of your marketing strategy. It's like a financial detective, uncovering clues to guide your next move and ensure your marketing dollars are working as hard as they can.
How to Calculate Rate of Return
The Rate of Return (RoR) is calculated by taking the gain or loss made from an investment, subtracting the original cost of the investment, and then dividing this figure by the original cost of the investment. The formula is:
The formula looks like this:
For example, if you bought shares for $1,000 and sold them for $1,200, your RoR would be calculated as follows:
RoR= (1200−1000/1000)× 100 % = 20 %
This result shows that the investment yielded a 20% return on the original investment.
The result is expressed as a percentage, representing the efficiency of an investment relative to its initial cost. This calculation can be applied to any type of investment and is useful for comparing the performance of different investments over a specific period.
How to automate ROI and ROAS calculation with OWOX BI
With OWOX BI, you can measure the effectiveness of your campaigns more deeply and automatically compare ROAS and ROMI, and display results on a dashboard in Google Sheets, or Looker Studio.
As a result, you’ll be able to make conclusions about the payback of a channel based on complete data and will be able to properly allocate your budget.
In order to have a complete picture while comparing ad channels, you need to:
- Set up data transfer from advertising services (Facebook, Google Ads, Twitter Ads, etc.) to Google BigQuery via OWOX BI Pipeline.
- Set up data transformations to merge this data with behavioral data from your website.
- Build attribution models (at least one).
- Just connect the data mart prepared with OWOX BI with a set of templates for Looker Studio we’ve prepared.

Lower Adwaste, Save Time, and Grow ROI
Make smart decisions about your campaign optimization faster
What is considered a good ROI?
So, you realize the importance of ROI calculation. But what should you do with the data you receive? What ROI is considered to be good and what is considered to be bad?
Every business has its own ideal ROI. But one rule applies to everyone: ROI must be positive, and ROAS must be above 100%.
When we're talking about what makes a 'good' ROI, it's kind of like asking, "How spicy do you like your food?" It depends on your taste – or in this case, how much risk you're comfortable with and how patient you are for your investment to pay off.
If you're the type who prefers to play it safe, a lower ROI might still look pretty good to you. It's like choosing a mild salsa instead of a super spicy one – you're okay with less 'heat' in exchange for peace of mind. On the flip side, if you're okay with waiting longer for your money to grow, you'll probably expect a higher ROI. It's like putting your money in a slow cooker; you're willing to wait because you're hoping for a more flavorful outcome.
So, a 'good' ROI isn't one-size-fits-all. It's all about what works for you – your risk appetite and your timeline.
By monitoring the dynamics of changes in ROI in reports, you can reallocate your advertising budget to more effective advertising channels.
Expanding the Scope of ROI: Beyond Traditional Metrics
As we dive deeper into expanding the scope of ROI beyond traditional metrics, it becomes crucial to discuss Marketing Statistics ROI – a tool that's reshaping how we evaluate the success of marketing strategies.
In the digital age, where every click, like, and share counts, Marketing Statistics ROI emerges as a game-changer. It's not just about how much money was made versus spent; it's about understanding the effectiveness of each marketing move in a digital playground that's constantly evolving.
Imagine launching a social media campaign. Traditional ROI would have us focus solely on the direct sales generated. But Marketing Statistics ROI urges us to look further. How many people engaged with your content? Did the campaign enhance your brand's visibility? These are the kinds of questions Marketing Statistics ROI helps answer.
This approach also lets us gauge the long-term impacts of marketing efforts. It’s not always about immediate sales; sometimes, it’s about building a brand story, creating loyal followers, or simply staying top of mind with your audience. Marketing Statistics ROI factors in these subtler, yet equally crucial, elements of marketing success.
In essence, Marketing Statistics ROI is a vital tool in the modern marketer’s arsenal. It acknowledges that in today's interconnected world, the impact of marketing is multifaceted and demands a broader, more nuanced lens for evaluation.
By embracing Marketing Statistics ROI, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their marketing efforts' true effectiveness, paving the way for more informed, strategic decisions that go well beyond the surface level of profit and loss.
Conclusion
Measuring the return on marketing and business investments is a must. These metrics will help you find out where you really should invest to earn more. You should start setting up data collection and calculating ROI from the moment you start thinking about business and marketing costs.
When calculating return on investment, you need to:
- Choose the right attribution model
- Define your income and costs
- Consider the full sales cycle
FAQ
-
When should I use ROI vs. ROAS?
Use ROI when you want a comprehensive view of an investment's profitability, including all associated costs and returns. It's suitable for overall business investments, project assessments, and broader financial decisions. Use ROAS for a focused evaluation of advertising campaigns, measuring the direct revenue return from specific marketing spends. -
Can ROI be too high?
While a high ROI is generally favorable, an extremely high ROI might indicate an underestimation of costs or an exceptionally high return that may not be sustainable in the long term. It's important to analyze high ROI figures critically to ensure they're realistic and account for all relevant factors. -
What is ROI and how is it calculated?
Return on investment measures the revenue attributed to a particular investment. -
What is a good ROI?
For different businesses, the figures are different: some businesses can make money with a very low ROI; others may need a relatively high ROI to avoid losing money on digital advertising. But one rule stands for all: return on investment must be positive (above 100%). -
What is a 50% ROI?
A 50% return on investment means that you get $0.5 for each $1 you’ve invested. -
What is a 100% ROI?
A 100% return on investment means that you’ve doubled your primary investment.













